
WHY IS E-COMMERCE IMPORTANT TO INDIA?
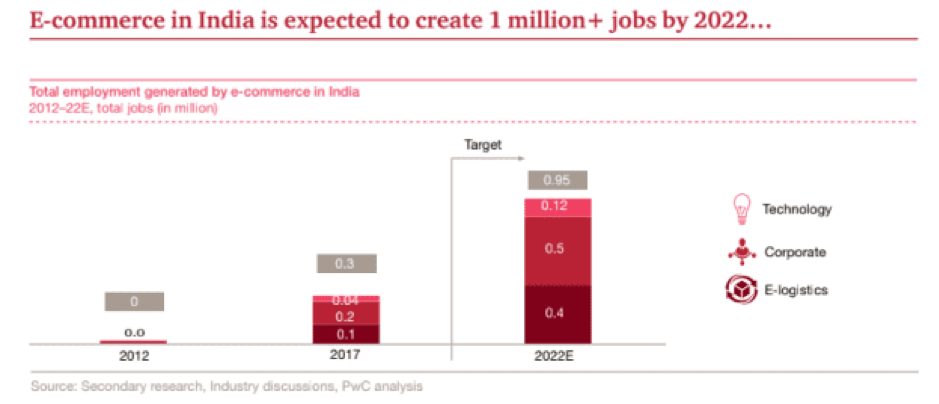
In 2018, India was named as the world’s fastest growing economy. The Indian retail industry contributes 10% to its GDP and 8% to total employment, the E-Commerce sector contributes only a mere 2% (projected to grow to 12% by 2026). Then why has the E-Commerce industry garnered so much attention from industry and policy-makers alike? Despite this small market penetration, the Indian E-Commerce sector is one of the top 10 fastest growing E-Commerce markets in the world. Research also indicates that the Indian E-commerce market can potentially create 1 mn + jobs by 2022. E-commerce is expected to not just create regular corporate jobs but also increase employment in allied industries like Logistics and Warehousing. For every job that is created by the E-commerce industry, further 3-4 jobs can get created in downstream industries.
It is not just the number of jobs that are being created by E-Commerce that is important but the type of jobs. Around 0.1 mn core jobs will focus on e-commerce technology, such as algorithms and the development of interfaces. Within ancillary jobs, e-logistics is expected to be the largest segment, creating more than 0.3 mn jobs. Delivery/last mile delivery will contribute to approximately two-thirds of the jobs as e-commerce grows beyond Indian metros. The dynamic nature of these jobs will propel the labour industry in diverse directions in the future. Development in technology will render many traditional jobs patterns in India redundant. For example, the influx of Electric Vehicles will witness a dip in employment in the auto sector and advances in AI technology will see an HR and Finance employment slow down.
WHY IS THE INDIAN E-COMMERCE MARKET IMPORTANT TO FOREIGN INVESTORS?
The potential of the E-Commerce market in India is well-known to Foreign investors. Indian E-Commerce is expected to surpass the United States to become the second largest E-Commerce market in the world. The market is expected to reach $ 100 bn by 2022 and $ 200 bn by 2026 from $ 38.5 bn as of 2017. With increasing internet penetration, eCommerce is India’s fastest growing and most dynamic channel for commercial transactions.
Some of the major developments in the India E-Commerce sector are:
- Walmart’s acquisition of Flipkart, an Indian E-Commerce platform, for $16 bn.
- Launch of the Paytm Payment Bank, India's first bank with zero charges on online transactions, no minimum balance requirement and free virtual debit card.
- 21 private equity and venture capital deals worth $ 2.1 bn in 2017 and six deals worth $ 226 mn in January-April, 2018 in the Indian eCommerce sector.
WHAT'S FEEDING THE INDIAN E-COMMERCE GIANT?
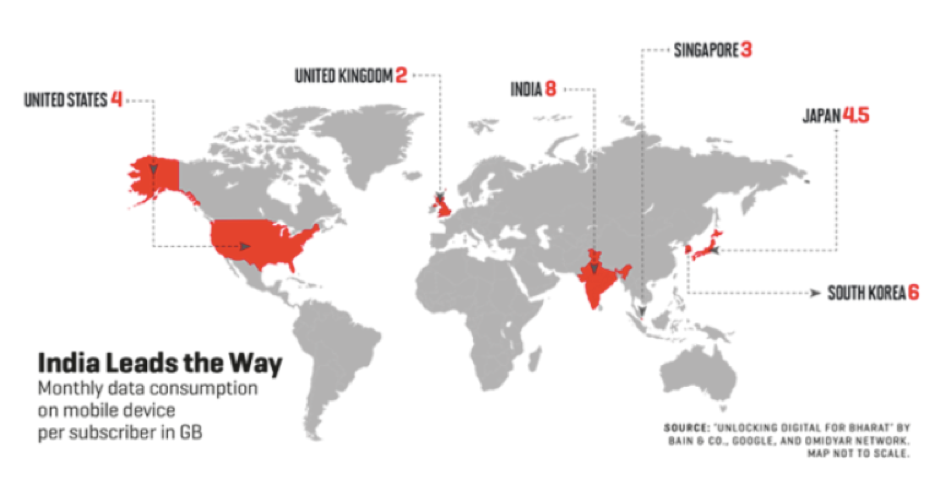
The rapid rise of E-Commerce in India is driven by a host of factors such as growing mobile subscribers, high rate of internet penetration, growing usage of credit cards, and India’s large young population. The Governments proactive attempts to encourage digital payments and extend the digital economy to rural areas of the country in the digital ecosystem act as additional catalysts. The factors driving eCommerce in India can be categorized as organic and inorganic demand drivers.
Organic demand drivers: Not only is India home to the 1.37 bn people but it is also the largest children’s population in the world with over 120 mn infants in the 0-4 age group. It is predicted that 75% of the population by 2020 will belong to the technologically aware Gen Z. This population growth is also complemented by changing affluence and by extension expenditure trends of consumers. India’s income pyramid has transformed itself into a diamond as household incomes grow. In terms of spending, the two top consumer categories—elite and affluent—will become the largest combined segment by 2025, accounting for 40% of consumption compared with 27% in 2016. The rapidly falling price of smartphones and fast growing internet penetration has seen a drastic increase in sales of smartphones. Studies indicate that by 2025, 60% of India’s population will have a smartphone and fast and reliable data connectivity and 450 mn of India’s buyers will be digitally influenced.
Inorganic demand drivers: Acknowledging the potential and impact of eCommerce the Government of India has taken drastic steps to ensure the continued growth of internet penetration and encourage the development of a digitally influenced population. The government’s JAM trinity initiative has linked over 736 mn bank accounts to Aadhar in an attempt to increase digitalized financial inclusion and encompassed over 450 mn internet users in India. Under the “Digital India” initiative GoI has enrolled over 8.1 mn individuals for digital literacy programs and set up 2.5 lakh Common Service Centres in rural India.
WHAT'S GOING ON WITH OUR POLICIES THEN?
The promising growth of e-commerce in India has been factoring in a number of domestic as well as international challenges, especially at the policy front. Even after touching the $ 20 mn mark in sales, and receiving the world’s biggest investment in the sector, India still has to finalize a comprehensive policy for this sector. It is in this light that the government decided to set up a think tank to prepare a national framework of E-commerce in April 2018. The think-tank circulated its first draft report to its stakeholders on 30 July 2018 with the objective of enabling the stakeholders to tap the opportunities that would arise from progressive digitalization of the domestic and global economy.
While straddling through various issues like international trade, domestic trade, competition policy, consumer protection, information technology, it is imperative that e-commerce thrives in a conducive environment promoting level playing field for both entrepreneurs and consumers. A comprehensive policy is the need of the hour to achieve more growth in this promising sector and clearly, the government is taking the right steps to meet this need.
- https://timesofindia.indiatimes.com/business/india-business/india-is-fastest-growing-e-commerce-market-report/articleshow/66857926.cms
- https://www.paymentscardsandmobile.com/the-fastest-growing-global-e-commerce-markets/
- https://www.globalpaymentsinc.com/-/media/nofollow/uk/sme-mnc-campaign-whitepaper/gppewhitepaperv5web.pdf?modified=20180620173439
- https://www.peoplematters.in/news/jobs/indias-ecommerce-market-can-create-over-1-mn-jobs-by-2023-report-19197
- https://www.pwc.in/assets/pdfs/publications/2018/propelling-india-towards-global-leadership-in-e-commerce/executive-summary.pdf






