Why Invest in Railways
-
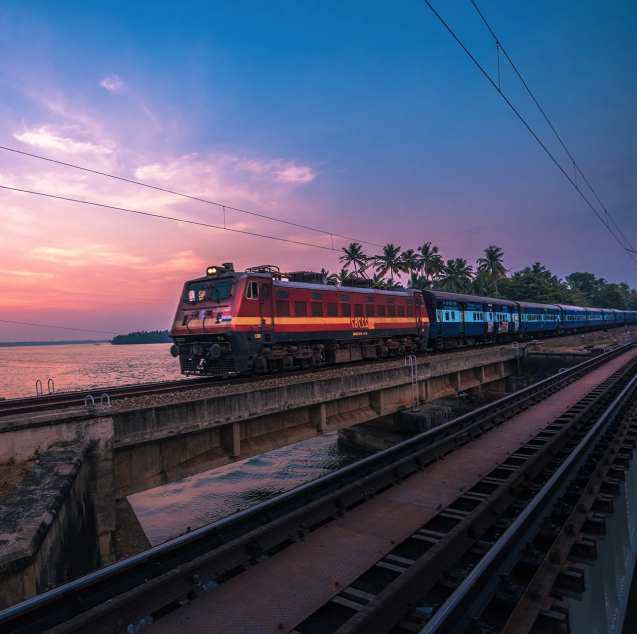
Passenger Growth
29% increase in rail passenger forecast from 2021 (9,457 Mn) to 2031 (12,213 Mn)
-
Freight Growth
157% increase in expected freight handled by Indian Railways from 2021(1,231 Mn Tonnes) to 2023 (3,167 Mn Tonnes)
-
Surge in Demand
The demand for rolling stock will surge by 25% from 2026 to 2031
-
Rolling Stock Expansion
The National Rail Plan 2030 states that the demand for locomotives, coaches and wagons will increase by 174%, 151% and 162% respectively over the next 25 years