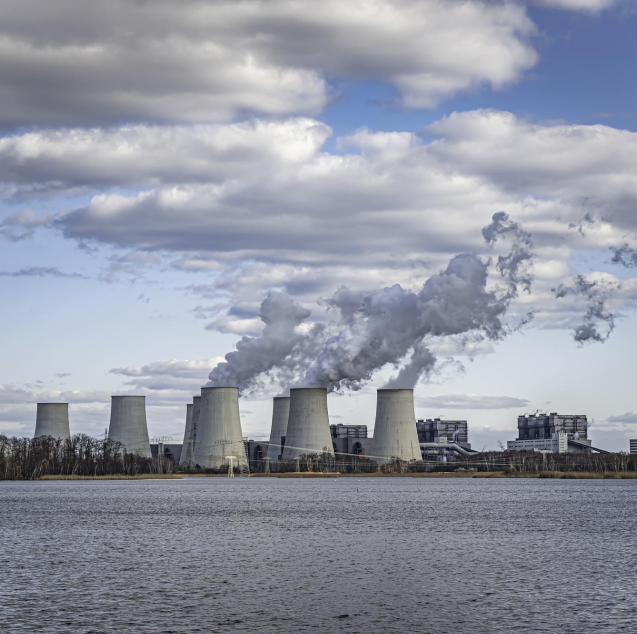
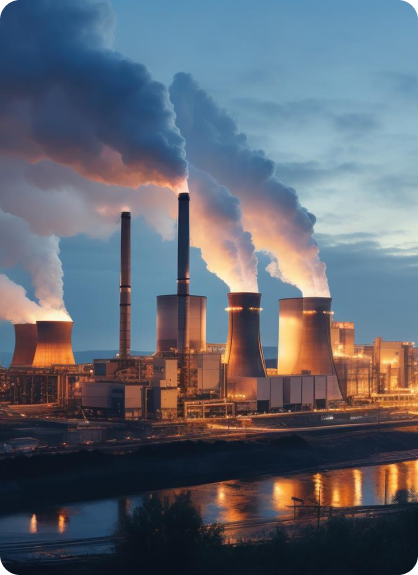
India's Thermal Power sector is a cornerstone of the nation's energy infrastructure, pivotal in meeting the country's burgeoning energy demands. As of November 2024, coal production in India has surged to 90.62 MT, underscoring the sector's critical role in powering the economy. Coal accounts for approximately 46.2% of India’s total installed power capacity, making it the backbone of the country's energy supply. This reliance on coal is necessary to ensure a stable and reliable power supply, essential for industrial growth and economic development.
The significance of the Thermal Power sector is further highlighted by the government's proactive measures to enhance production and efficiency. According to the Ministry of Coal, recent policy reforms and the introduction of advanced technologies have significantly boosted production capacities and supply chains. For instance, initiatives such as the Coal Mines (Special Provisions) Act have streamlined the allocation and operational processes, facilitating higher production rates and better resource management. Additionally, the government's emphasis on maintaining adequate coal stocks at thermal power plants has resulted in a stockpile sufficient to meet 19 days of demand, ensuring energy security during peak consumption periods.
Moreover, the sector is undergoing a transformation with a focus on integrating renewable energy sources. The Ministry of Power has been working on balancing the energy mix by promoting the use of renewable energy alongside traditional thermal power. This strategic approach aims to create a sustainable and environmentally friendly energy framework. Efforts are being made to modernize thermal power plants with advanced emission control technologies to meet global environmental standards. The implementation of supercritical and ultra-supercritical technologies is one such example, which enhances efficiency and reduces greenhouse gas emissions.
Despite the high demand for power, India has managed to maintain a robust supply chain, ensuring continuous and uninterrupted power delivery. The government’s focus on infrastructure development, such as improving coal transportation and logistics, has played a significant role in this achievement. Additionally, investments in modernizing existing power plants and constructing new ones are set to further bolster the sector’s capacity.
India's rapid economic growth necessitates a dependable and efficient power sector. The Thermal Power sector's ability to meet rising energy demands is crucial for sustaining industrial activities and overall economic progress. The sector not only supports large-scale manufacturing and services but also underpins the daily lives of millions of citizens by providing reliable electricity.