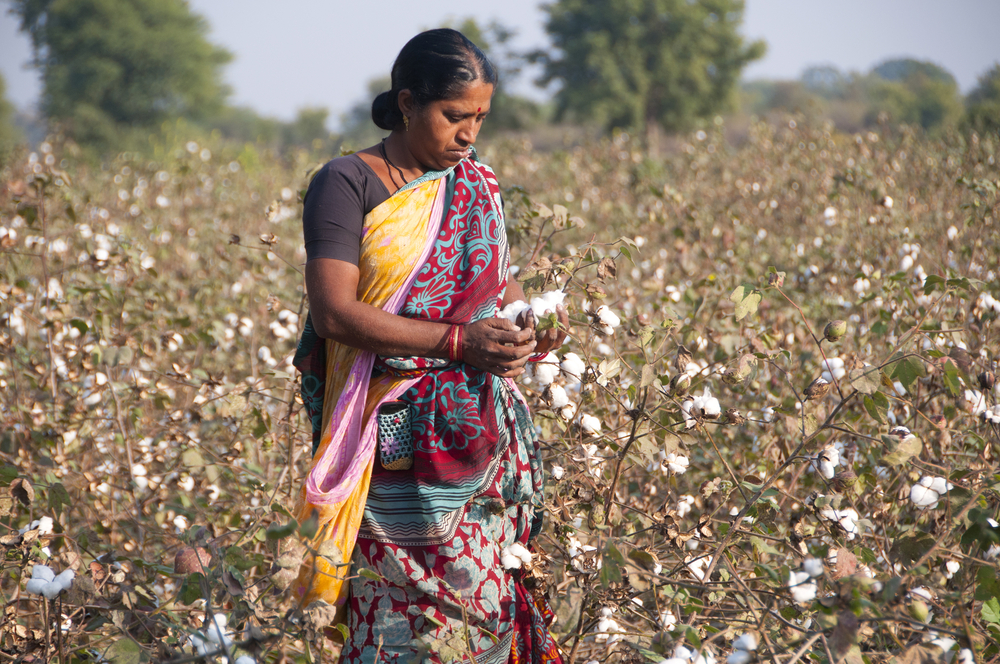
Introduction of cotton production in India
One of mankind’s great discoveries, cotton is one commodity that is available virtually everywhere - testifying both to its utility, as well as the awe-inspiring impact capitalism, has had on human production and consumption. Cotton production in India has focused on textiles for over thousands of years, generating significant employment for both skilled and unskilled labour - thus helping strengthen the country’s economy.
The cotton sector in India is considered the second most developed sector in the textile industry (after man-made fibres). At 18% of the global total, India is the world’s largest producer of cotton. It also has the largest area under cotton cultivation in the world, representing about 25% of the world’s area under cultivation. The states of Gujarat, Maharashtra, Andhra Pradesh, Haryana, Punjab, Madhya Pradesh, Rajasthan, Karnataka and Tamil Nadu are the major cotton producing areas in India.
History of Cotton Textile Industry in India

The history of the cotton industry in India dates back millennia. India held a global monopoly over the manufacturing of cotton textiles for about 3,000 years - from 1500 B.C. to 1500 A.D. It served as an ideal medium of exchange in the barter economy during the ancient period. During the middle ages, it was exported to Eastern and European markets. This was followed by the establishment of cotton mills by imperial powers in the modern period.
The first cotton mill in India was established in 1818 at Fort Gloster near Kolkata but was a commercial failure. The second cotton mill in India was established by KGN Daber in 1854 and was named Bombay Spinning and Weaving Company. This mill is said to mark the true foundation of the modern cotton industry in India. In Ahmedabad - also referred to as the ‘Manchester of India’ - the opening of Shahpur mill in 1861 and Calico mill in 1863 marked the city’s spectacular rise as one of the world’s prime cotton manufacturing locales.
However, the real expansion of the cotton textile industry in India took place in the 1870s. During this period, the number of mills rose to 47 - of which over 60 % were in Mumbai. The First and Second World Wars, the Swadeshi Movement and the grant of fiscal protection rapidly propelled the growth of this industry. As a result, the number of mills increased from 334 in 1926 to 389 in 1939, and to 417 in 1945. Production of cotton cloth also increased from 4,012 million yards in 1939 - 40 to 4,726 million in 1945 - 46.
Market size and growth of the cotton textile industry in India

Cotton production in India increased from 119 lakh bales in 1991 - 92 to 345 lakh in 2016 - 17, a growth of 190%. Nearly two - thirds of cotton production in India comes from the states of Maharashtra, Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh and Telangana - collectively known as the Cotton Basket of India. In FY 2017, India contributed 26% to total global harvested cotton. It ranked before China, which supplied 21%. Approximately 62% of India’s cotton is produced in rainfed areas, and 38% on irrigated lands. India grows all four known species of cultivated cotton.
The cotton industry in India leans towards apparel exports, contributing approximately 51% to overall apparel exports in FY 18. Approximately 74% of the apparel exported from India is made of cotton.
Cotton is freely exportable from India, with major export destinations being US, Bangladesh, China, Vietnam, Pakistan, Indonesia, Taiwan and Thailand, among others. Bangladesh has been the largest importer of Indian cotton since FY 2015. India's cotton exports are expected to jump 43% to 10 million bales (of 170 kg each) in 2018 - 19; this is due to strong overseas demand, especially from China.
Cotton made - ups ($ 47.03 bn) accounted for 40.10% share in the global trade of cotton textiles. Meanwhile, cotton fabrics ($ 56.53 bn) and cotton yarns ($ 13.73 bn) accounted for 48.19% and 11.71% of total world trade in these items respectively.
Between Apr - Oct 2018, total textile and clothing exports stood at INR 1.52 tn ($ 21.95 bn). During the same period, exports of raw cotton including waste, cotton yarn, cotton fabrics and cotton made - ups grew by 26.01%, to $ 6,893.05 mn from $ 5,470.20 mn.
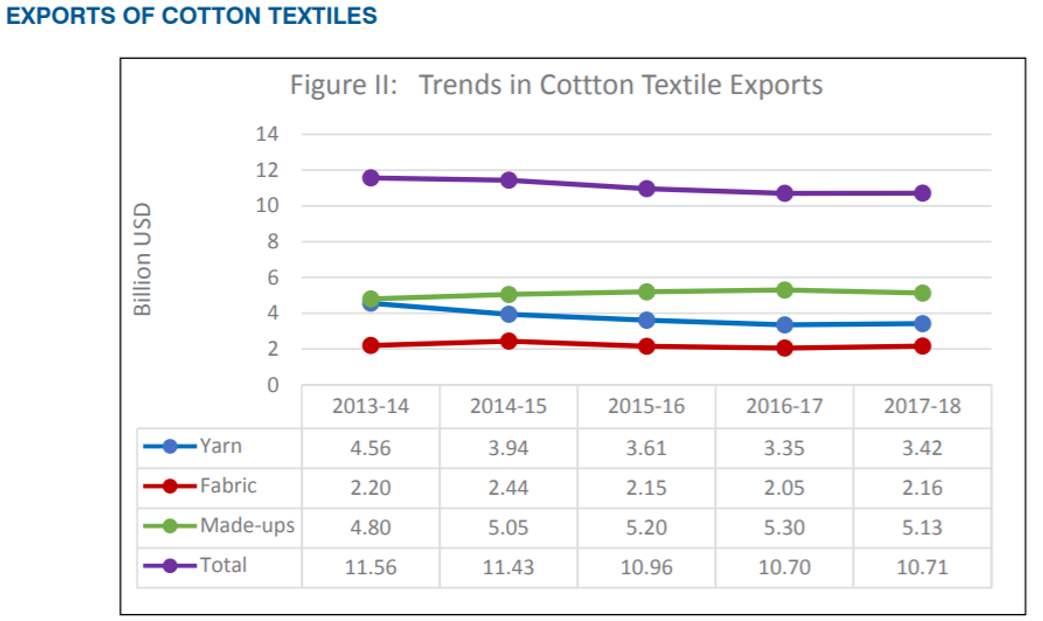
Observed Trends
• In 2017 - 18, exports of cotton textiles from India marginally increased by 0.09% to $ 10.71 bn from $ 10.70 bn in 2016 - 2017
• Exports of cotton yarns grew by 2.08% in value terms during 2017 - 18
• Cotton made - ups showed a decline of (-) 3.20% in value terms
• Cotton fabrics reported a growth of 5.36% during the fiscal year 2017 - 18
Following are the reputed foreign retailers and brands that import products from the cotton industry in India:

Economy Contribution
• India is the world’s largest cotton producer, accounting for ~38% of global cotton acreage and ~23% of global cotton production.
• It is also the second largest exporter (after the USA) and the second largest consumer (after China).
• Within the country, Maharashtra has the highest area under cultivation, at 41.2 lakh ha, followed by Gujarat at 27.1 lakh and Telangana at 17.9 lakh. Together, these three states account for 72% of the total cotton acreage in the country.
• The decline in production has also resulted in a significant decline in the closing stock of the cotton market in India. It was 8.5 mn bales as on Mar ’19, compared to 12.6 mn during the same period last year. Owing to the increase in cotton prices vis - à - vis other crops like soybean and paddy, acreage is likely to shift towards cotton in 2019 - 20 ($A estimates 3.2% YoY rise in acreage).
• The cotton market in India is likely to recover from the subdued 2018 - 19 cotton season, during which yield declined by 11%. Production in 2019 - 20 is estimated to grow ~17%, as both yield and acreage rebound.
Latest Developments

According to the Ministry of Textiles’ Cotton Textiles Export Promotion Council (TEXPROCIL), there was a 26% growth in cotton textile exports between April - September 2018. TEXPROCIL has also proposed to include cotton yarn, a value - added product, under the Merchandise Exports from India Scheme (MEIS) to boost the cotton textile industry in India.
Government of India has been rendering support to the cotton textile sector through initiatives such as Scheme for Integrated Textile Parks (SITP), Integrated Skill Development Scheme (ISDS), Integrated Processing Development Scheme (IPDS), Market Development Assistance (MDA) and Market Access Initiative (MAI). Another push to Amended Technology Upgradation Fund Scheme (ATUFS) has been provided under the special package of INR 6,000 cr for the made - ups and garments sector.
- https://bettercotton.org/where-is-better-cotton-grown/better-cotton-in-india/
- http://www.yourarticlelibrary.com/industries/cotton-textile-industry-in-india-production-growth-and-problems/19704
- https://economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/economy/foreign-trade/cotton-exports-likely-to-jump-43-in-2018-19/articleshow/64586458.cms
- https://www.ibef.org/exports/cotton-industry-india.aspx
- http://www.indiantradeportal.in/vs.jsp?lang=1&id=0,30,50,168







