Industrial Park Rating System (IPRS) is an extension of the India Industrial Land Bank (IILB) platform which features more than 4,500 industrial parks and is a GIS-enabled database to facilitate investors to identify their preferred location for investment. IILB is currently integrated with the industry-based GIS system of 34 states and union territories.
Under, “Atma-Nirbhar Bharat Abhiyan”, DPIIT launched the Industrial Park Rating System (IPRS) and organized a pilot level exercise in 2018 with the support of the Asian Development Bank (ADB) and the Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) aiming to rate the country’s industrial parks and special economic zones.
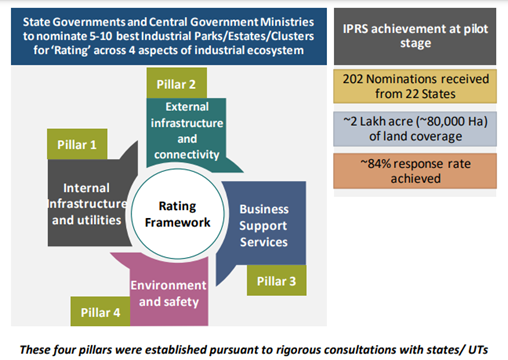
The pilot rating framework was conceptualized across four pillars— internal infrastructure and utilities, external infrastructure and facilities, business support services, and environment and safety management. These pillars were assessed across 34 parameters finalized in discussion with DPIIT and various stakeholders of the Industrial Information System (IIS). This exercise provided vital insights regarding factors that drive industrial competitiveness. These 34 areas of inquiry were supported by 27 additional or supplementary questions totaling 61 questions. Out of the 202 nominated parks under the pilot phase, 177 parks across 21 states were evaluated based on the above pillars and parameters.
Industrial Park Rating System Report 2.0
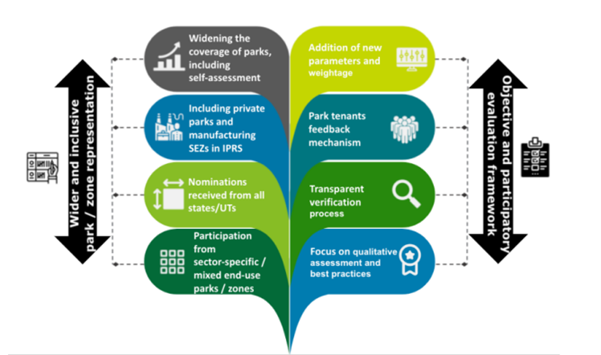
Based on the findings of the pilot and review of the global approaches, frameworks, and guidelines (adopted to develop inclusive and sustainable industrial parks), DPIIT with the support of Invest India, ADB, and MeitY, introduced ‘IPRS 2.0’ as a key enabler for identifying additional measures to enhance industrial competitiveness. DPIIT adopted an extensive consultative process to fine-tune the IPRS framework. In line with this step, DPIIT organised a consultation workshop on IPRS 2.0 that saw participation from various states/UTs/central departments and other stakeholders. Further, periodic meetings were also held with the steering committee.
Globally known frameworks were referred for developing the initial concept of IPRS 2.0 viz. the International Guidelines for Industrial Park (IGIP) developed by United Nations Industrial Development Organization (UNIDO), and the Eco-Industrial Park (EIP) framework developed by UNIDO, World Bank, and GIZ. Compared with the 34-parameters assessment framework used for the pilot phase, 45 parameters were developed for the assessment of industrial parks and 40 parameters separately for SEZs under the four pillars for IPRS 2.0.
The report includes 449 industrial parks and SEZs assessed and rated out of 478 nominations by 31 participating States and UTs, including 51 private parks and SEZs rated. Feedbacks from developers as well as tenants was included in this phase. Parks nominated where response was received from more than 15 percent tenants (365), Leaders: 41 industrial parks and 13 SEZs, Challengers: 90 industrial parks and 17 SEZ, and Aspirers: 185 industrial parks and 19 SEZs.
Parks nominated where response was received from less than 15 percent tenants (84), Leaders: 27 industrial parks, Challengers: 18 industrial parks and 1 SEZ, and Aspirers: 38 industrial parks.
To further enhance the scope of the framework and make the industrial rating process more scientific in nature, ‘IPRS 2.0 Gap Assessment Report’ will be prepared by ADB in consultation with Invest India under the guidance of DPIIT for each participating State/ UT (31). The report will highlight global and local best practices, interventions required by States/ UTs along with potential funding avenues to bridge the gaps. The report will also provide the differentiated outcomes for all stakeholders involved.
The format shall be a mix of workshops with field visits to select Industrial Parks/Zones including physical/virtual workshops with State Industrial Development Corporations (SIDCs) senior officials led by DPIIT along with teams from Invest India and ADB. Capacity building workshops will also be held in association with UNIDO/ADB for SIDCs and other stakeholders.
This blog has been co-authored by Vrinda Tanwani



