Introduction to the Service Sector in India
The growth of the Services Sector in India is a unique example of leap-frogging traditional models of economic growth. Within a short span of 50 years since independence, the contribution of the service sector in India to the country’s GDP is a lion’s share of over 60%. However, it still employs only 25% of the labour force. Consequently, agriculture (which is stagnant) and manufacturing (which has not yet risen to its full potential) continue to sustain the majority of our employed population. This presents a unique challenge to future economic growth in India and requires out of the box solutions that will help rapidly harness the potential of the service industry in India. Invest India takes a look at the contribution of the services sector in the Indian economy, its successes and also explores potential enablers for future equitable economic growth.
Market Size of Service Industry
A quick comparison with the American and Chinese economy reveals the unique nature of India’s GDP growth from the contribution of the Service sector and its linkages to employment and income distribution (Figures in bracket indicate employment). Over time, a robust manufacturing and productive agriculture sector leads to the Service industry in India becoming the mainstay of GDP and employment. In our context, the Service sector has become extremely important to grow not only our GDP, as well as make it the key vehicle for employment generation. However, the question is - how to increase value add to GDP from Service companies in India, while reducing employment dependency from agriculture, as well as boosting the manufacturing industry.
|
India |
China |
||
|
Agriculture and Allied |
15.4% (53%) |
8% (2%) |
7% (26%) |
|
Manufacturing and Industry |
23% (22%) |
12% (19%) |
40% (28%) |
|
Services* |
61.5% (25%) |
80% (79%) |
52% (46%) |
(*IT contributes the majority)
The current growth of service sector in India is based mainly on labour market arbitrage. Moving forward, India can no longer rely on ‘low cost’ for ‘low value added’ services. Therefore, we need solutions that address these:
i) Boosting the manufacturing sector with both direct and indirect spin - off benefits for the growth of the service sector in India (e.g. Make in India)
ii) Moving up the value chain, especially in the IT/ ITeS sector.
iii) Broad - basing the Indian Services offering platform into sectors beyond the traditional IT/ ITeS by identifying the global demand for such services, and meeting these demands based on our natural competencies and comparative advantages.
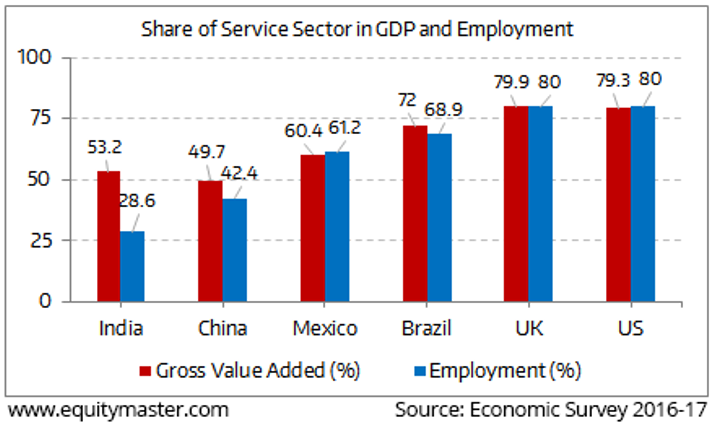
Comparison – GDP in Service sector and Employment generation
Service Sector in India: Sectors and Growth potential
Let us now look at the list of service sectors in India that perform, as well as demonstrate strong potential for future growth.
IT-BPM/ Fintech
The IT/ITeS & Fintech segments provide over $ 155 bn in gross value add and have the potential to grow between 10 -15% p.a. Exports form its largest component. So far, our key advantage has been low - cost labour arbitrage in a predominantly English - speaking country. Going forward, the IT and ITeS segments require significant upskilling to move beyond a ‘low - cost low value add service provider’ to a ‘high value add partner’.
Indian IT companies can also leverage their skill sets to provide fintech solutions to global financial customers. Financial risk management services, insurance, natural disaster modelling and underwriting are examples of high value add services performed within India for a global audience.
Healthcare & Tourism
The current contribution of the healthcare industry is over $ 110 bn and is expected to touch $ 280 bn by 2020. Availability of world - class medical facilities, skilled doctors, technicians and pharmaceuticals are some of our advantages. With digital communication and interfaces, diagnostic medicine can also be tapped into as a service for global customers.
Similarly, for tourism, India is renowned for its places of natural beauty and historical significance. Tourism presently contributes $ 47 bn to the country’s GD, compared with $ 115 bn for China. Thus, tourism has exponential possibilities to boost the Indian services sector in the next decade.
To attract significant revenues, improved customer experience (medical or tourism) is the key factor that will determine its future growth. In this context, government initiatives such as e - Visas, better infrastructure facilities, safety, connectivity etc. are enablers in the right direction.
Space
India captured the world's attention last February when it broke the record for launching the most number of satellites into space. Moreover, this was done at a fraction of the cost incurred by other space powers.
Indian services in the space domain, with proven expertise in multiple launch technologies, provide it with a significant advantage over its peers in the global space transportation industry. Our launch capabilities have a near 100% track record. Many countries are actively looking to piggyback on India’s launch facilities. This demonstrates great potential. The government is actively proving its ability, but more can be done to build capacity in military and non - military space applications. In this context, public - private participation is key to ensure the flow of capital, as well as to strengthen competencies in this area.
Logistics & Transportation
India’s natural coastline and vast river network give it a competitive edge in providing transportation and logistics services, both domestically and internationally. These can be classified into ports and ports services, warehousing, trans - shipment services, e - logistics, inland waterways for freight and passengers, expressways and dedicated freight corridors. India’s logistics service sector itself is expected to grow from $ 115 bn to $ 360 bn by 2032.
India should closely look into the development of the service industry, given the potential and need for sustained large scale investment. Investments typically have a long gestation period. However, once the infrastructure is created, linkages to the rest of the economy provide significant multiplier effects. For example, the Mumbai - Pune expressway and the development of service industries in Pune.
Other services
Media & Entertainment (animation, gaming, dubbing), Education (online platforms such as MOOC), and Sports (IPL, IFL, Sports Management), Legal/ Paralegal services, Risk management and advisory functions, etc. are areas that can lead to an immense contribution of service industry in the Indian economy.
Top 10 service sector companies in India:
|
1 |
Reliance Industries |

|
|
2 |
HDFC Bank |

|
|
3 |
ICICI Bank |

|
|
4 |
HDFC |

|
|
5 |
Tata Consultancy Services |

|
|
6 |
Larsen & Toubro |

|
|
7 |
State Bank of India |

|
|
8 |
NTPC |

|
|
9 |
Kotak Mahindra Bank |

|
|
10 |
Axis Bank |

|
Recent Investments in the service sector

Of late, the government’s efforts in improving ease of doing business and relaxing regulatory norms have resulted in increasing FDI into the country. The following examples demonstrate the strong linkages that FDI has in unleashing the potential, as well as propelling the growth of the services sector in India:
- Connecting Gujarat and Maharashtra, India’s first bullet train has potential similar to that of the Mumbai - Pune expressway, but on a larger scale.
- Manufacturing of Rafale jets in India.
- Building large highway systems in India (expressways and freight corridors), inland waterways (Jalmarg Vikas project), port modernisation and new port development (Sagarmala project)
-Amazon India expanding its logistics footprint
-Creation of a Taiwanese tech park in Karnataka
-A dedicated fund of $ 693 mn, which will be utilized to support sectoral undertakings under the Champion Services Sectors Initiative. These include IT and ITeS, Tourism and Hospitality Services, Medical Value Travel, Transport and Logistics Services, Accounting and Finance Services, Audio Visual Services, Legal Services, Communication Services, Construction and Related Engineering Services, Environmental Services, Financial Services and Education Services.
Future Prospects of the Service Sector in India
The service sector in India has the highest employment elasticity among all sectors. Thus, it has the potential for huge growth as well as the capability to deliver highly productive jobs - leading to revenue generation. To address the challenge of job creation, the Skill India program aims to achieve its target of skilling/ up - skilling 400 million people by 2022. It aims to do this mainly by fostering private sector initiatives in skill development programs, and by providing them with the necessary funding.
Similarly, the Make in India program - while attempting to bolster the manufacturing sector - will cause a multiplier effect in adding to the portfolio of the Service Sector. In this context, the Startup India initiative is a key enabler for both the manufacturing as well as service industry in India - by offering to support innovative startups.